Bounce houses are a fantastic way to bring life and excitement to any event, be it a birthday party, family gathering, or community event. When purchasing a bounce house, it’s essential to understand the different materials available and their unique properties. PVC tarpaulin, vinyl, and Oxford fabric are commonly used materials in the industry. In this article, we’ll dive into the differences between these materials, their pros and cons, and some frequently asked questions to help you make an informed decision.
What Is PVC Tarpaulin?
PVC tarpaulin, often referred to as PVC tarp or vinyl tarps, is a robust, flexible, and waterproof plastic material. It’s crafted by combining PVC films with a polyester base fabric, creating a versatile material perfect for various applications.

There are three main types of PVC tarpaulin structures: 2-layer, 3-layer, and 4-layer. The 2-layer structure consists of a single PVC film layer and a base fabric layer made from materials like polyester, cotton, nylon, fiberglass, or a blend of these. Meanwhile, the 3-layer structure features two PVC film layers with the base fabric sandwiched in between. The 4-layer structure adds a black layer to the 3-layer structure, placed between the two PVC film layers, providing additional durability and strength.
| TYPES | PICTURE | STRUCTURE | COMPONENT | APPLICATION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Economical | 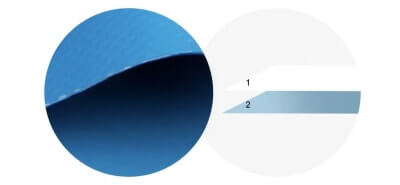 |
2-layer | 1. polyvinyl chloride film 2. Base fabric |
bags, gym mats |
| pop | 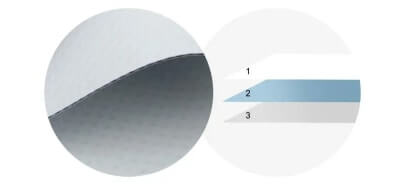 |
3-layer | 1. polyvinyl chloride film 2. Base fabric 3. polyvinyl chloride film |
banners, tarps, covers |
| Premium | 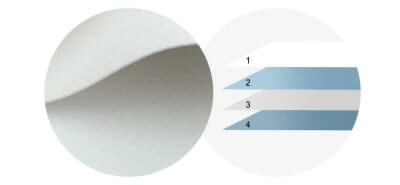 |
4-layer | 1. polyvinyl chloride film 2. Black layer 3. Base fabric 4. PVC film |
banners, tent(blockout light) |
The most commonly used type of PVC tarpaulin for bounce houses is the 3-layer structure. You’ll commonly find PVC tarpaulin thicknesses ranging from 0.4mm to 0.6mm (15 to 22 oz/yd²) and weights between 450 to 610 gsm. The choice of thickness and weight depends on factors such as the intended application, desired durability, and ease of handling.
A thicker and heavier PVC tarpaulin offers better durability and puncture resistance, making it ideal for commercial bounce houses or heavy-duty applications. This type of tarpaulin can withstand frequent use and provides a more robust structure.
On the other hand, a thinner and lighter PVC tarpaulin might be more suitable for residential bounce houses or inflatables used occasionally. While it is more lightweight and easier to handle, it may not be as durable as its thicker counterpart. When selecting the right PVC tarpaulin for your bounce house, consider both the desired durability and ease of handling to find the perfect balance.
Pros:
- Highly durable and resistant to wear and tear
- Water-resistant, making it suitable for wet environments
- Easy to clean and maintain
Cons:
- Heavier than Oxford fabric
- Less breathable, which may lead to higher temperatures inside the bounce house
What is Oxford Fabric?
Oxford fabric is a lightweight, breathable material made from woven polyester. It is a cost-effective alternative to PVC tarpaulin and vinyl, offering excellent durability and resistance to wear.

There are different grades of Oxford fabric that vary in thickness, weight, and denier count, which refers to the fabric’s yarn thickness. The denier count, commonly represented as “D,” indicates the weight and thickness of the fabric. Higher denier counts result in thicker, more durable fabrics.
For bounce houses, Oxford fabric typically ranges from 210D to 1680D. Here are some common denier counts and their corresponding characteristics:
- 210D: Lightweight, thinner, and suitable for residential bounce houses or inflatables used occasionally. Offers less durability but is easier to handle and transport.
- 420D: Medium-weight, offering a balance between durability and ease of handling. Suitable for residential use and some commercial applications.
- 600D: Heavier and thicker, providing increased durability and abrasion resistance. Commonly used for commercial bounce houses and inflatables.
- 1000D-1680D: The heaviest and thickest Oxford fabric, ideal for heavy-duty commercial bounce houses or inflatables that require exceptional durability and strength.
Pros:
- Lightweight and easy to transport
- Breathable, making it suitable for hot or dry environments
- More affordable than PVC tarpaulin and vinyl
Cons:
- Less water-resistant than PVC tarpaulin and vinyl
- May not be as durable in extreme conditions
Comparison Table for Pvc Tarpaulin and Oxford Fabric
| FEATURE | PVC TARPAULIN | OXFORD FABRIC |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | PVC films and polyester base fabric | Woven polyester fibers with a coating |
| Common Thickness | 0.4mm – 1.2mm | 210D – 1680D (denier count) |
| Durability | Highly durable, tear-resistant | Durable, abrasion-resistant |
| Water Resistance | Waterproof | Water-resistant to waterproof |
| Fire Resistance | Fire-resistant with fire retardant | Fire-resistant with fire retardant |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Maintenance & Cleaning | Easy to clean and maintain | Easy to clean and maintain |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | More affordable |
| Common Applications | Commercial and heavy-duty bounce houses | Residential and light commercial use |
This table provides a comparison between PVC tarpaulin and Oxford fabric, two common materials used in the construction of bounce houses. The table outlines differences in composition, thickness, durability, water resistance, fire resistance, weight, maintenance, cost, and common applications for both materials.
FAQs
Q1: Are PVC, vinyl, and Oxford fabric safe for children?
Yes, PVC, vinyl, and Oxford fabric used in inflatable bounce houses are designed to be safe for children. Manufacturers take safety into account when producing inflatables and often use lead-free, phthalate-free materials that meet industry safety standards.
Q2: What are the differences between PVC tarpaulin, vinyl, and Oxford fabric bounce houses?
PVC tarpaulin and vinyl are both durable, water-resistant materials, while Oxford fabric is a lighter, more breathable option. Each material has its advantages and drawbacks, so consider factors like climate, usage patterns, and budget when choosing the right material for your bounce house.
Q3: How do I maintain a bounce house made from PVC tarpaulin, vinyl, or Oxford fabric?
Regular cleaning and maintenance are essential to keep your bounce house in great condition, regardless of the material used. Follow these steps for proper care:
- Sweep and vacuum: Remove any debris or dirt by sweeping and vacuuming the bounce house’s surface.
- Clean with mild soap and water: Use a mild soap and water solution to gently clean the surface. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive tools that could damage the material.
- Rinse thoroughly: Rinse the bounce house with clean water to remove any soap residue.
- Dry completely: Allow the bounce house to air dry completely before folding or storing it. This helps prevent mold and mildew growth.
- Inspect and repair: Regularly inspect your bounce house for any signs of wear or damage. Patch small holes or tears using a repair kit designed for the specific material of your inflatable.



